DNA motors
DNA motors use the enerygy of ATP hydrolysis to processively translocate DNA between cellular compartments or within different cells, and belong to the large and diverse AAA+ family of enzymes. AAA+ motors form multimeric rings in which ATP hydrolysis and mechanical work are closely coupled. In general, we are interested in understanding the larger network of genetic interactions affecting the process of DNA transport in vivo. In particular, we want to understand the general mechanisms governing translocation directionality, transduction of energy into movement, and complex assembly. Click here for more information on SpoIIIE and FtsK.
Recruitment, Assembly, and Molecular Architecture of the SpoIIIE DNA Pump Revealed by Superresolution Microscopy.
|
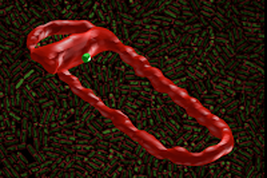
Here, we use photo-activated localization microscopy, structured illumination microscopy, and fluorescence fluctuation microscopy to investigate the mechanism of recruitment and assembly of the SpoIIIE pump and the molecular architecture of the DNA translocation complex. We find that SpoIIIE assembles into ∼45 nm complexes that are recruited to nascent sites of septation, and are subsequently escorted by the constriction machinery to the center of sporulation and division septa. SpoIIIE complexes contain 47±20 SpoIIIE molecules, a majority of which are assembled into hexamers. Finally, we show that directional DNA translocation leads to the establishment of a compartment-specific, asymmetric complex that exports DNA. Our data are inconsistent with the notion that SpoIIIE forms paired DNA conducting channels across fused membranes. Our results support a model in which DNA translocation occurs through an aqueous DNA-conducting pore that is structurally maintained by the divisional machinery, with SpoIIIE acting as a checkpoint preventing membrane fusion until completion of chromosome segregation. Our findings and proposed mechanism are relevant to the understanding of bacterial cell division, and may illuminate the mechanisms of other complex machineries involved in DNA conjugation and protein transport across membranes. See news feeds and more information here and here.
|
Direct observation of the translocation mechanism of transcription termination factor Rho
|
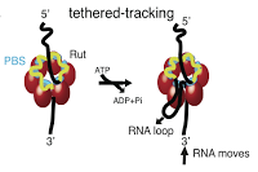
Rho is a ring-shaped, ATP-fueled motor essential for remodeling transcriptional complexes and R-loops in bacteria. Despite years of research on this fundamental model helicase, key aspects of its mechanism of translocation remain largely unknown. Here, we used single-molecule manipulation and fluorescence methods to directly monitor the dynamics of RNA translocation by Rho. We show that the efficiency of Rho activation is strongly dependent on the force applied on the RNA but that, once active, Rho is able to translocate against a large opposing force (at least 7 pN) by a mechanism involving 'tethered tracking'. Importantly, the ability to directly measure dynamics at the single-molecule level allowed us to determine essential motor properties of Rho. Hence, Rho translocates at a rate of ∼56 nt per second under our experimental conditions, which is 2-5 times faster than velocities measured for RNA polymerase under similar conditions. Moreover, the processivity of Rho (∼62 nt at a 7 pN opposing force) is large enough for Rho to reach termination sites without dissociating from its RNA loading site, potentially increasing the efficiency of transcription termination. Our findings unambiguously establish 'tethered tracking' as the main pathway for Rho translocation, support 'kinetic coupling' between Rho and RNA polymerase during Rho-dependent termination, and suggest that forces applied on the nascent RNA transcript by cellular substructures could have important implications for the regulation of transcription and its coupling to translation in vivo.
|
Nucleic Acids Res.
2015 Feb 27;43(4):2367-77. |
SpoIIIE mechanism of directional translocation involves target search coupled to sequence-dependent motor stimulation.
|
SpoIIIE/FtsK are membrane-anchored, ATP-fuelled, directional motors responsible for chromosomal segregation in bacteria. Directionality in these motors is governed by interactions between specialized sequence-recognition modules (SpoIIIE-γ/FtsK-γ) and highly skewed chromosomal sequences (SRS/KOPS). Using a new combination of ensemble and single-molecule methods, we dissect the series of steps required for SRS localization and motor activation. First, we demonstrate that SpoIIIE/DNA association kinetics are sequence independent, with binding specificity being uniquely determined by dissociation. Next, we show by single-molecule and modelling methods that hexameric SpoIIIE binds DNA non-specifically and finds SRS by an ATP-independent target search mechanism, with ensuing oligomerization and binding of SpoIIIE-γ to SRS triggering motor stimulation. Finally, we propose a new model that provides an entirely new interpretation of previous observations for the origin of SRS/KOPS-directed translocation by SpoIIIE/FtsK. See news feeds and more information here.
|
Structure and DNA binding properties of the Bacillus subtilis SpoIIIE DNA translocase revealed by single-molecule and electron microscope
|
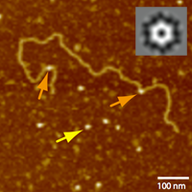
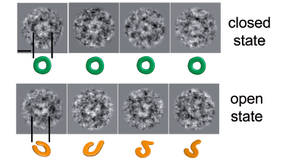
SpoIIIE/FtsK are a family of ring-shaped, membrane-anchored, ATP-fuelled motors required to segregate DNA across bacterial membranes. This process is directional and requires that SpoIIIE/FtsK recognize highly skewed octameric sequences (SRS/KOPS for SpoIIIE/FtsK) distributed along the chromosome. Two models have been proposed to explain the mechanism by which SpoIIIE/FtsK interact with DNA. The loading model proposes that SpoIIIE/FtsK oligomerize exclusively on SpoIIIE recognition sequence/orienting polar sequences (SRS/KOPS) to accomplish directional DNA translocation, whereas the target search and activation mechanism proposes that pre-assembled SpoIIIE/FtsK hexamers bind to non-specific DNA, reach SRS/KOPS by diffusion/3d hopping and activate at SRS/KOPS. Here, we employ single-molecule total internal reflection imaging, atomic force and electron microscopies and ensemble biochemical methods to test these predictions and obtain further insight into the SpoIIIE–DNA mechanism of interaction. First, we find that SpoIIIE binds DNA as a homo-hexamer with neither ATP binding nor hydrolysis affecting the binding mechanism or affinity. Second, we show that hexameric SpoIIIE directly binds to double-stranded DNA without requiring the presence of SRS or free DNA ends. Finally, we find that SpoIIIE hexamers can show open and closed conformations in solution, with open-ring conformations most likely resembling a state poised to load to non-specific, double-stranded DNA. These results suggest how SpoIIIE and related ring-shaped motors may be split open to bind topologically closed DNA.
|